|
Summary of what lies below
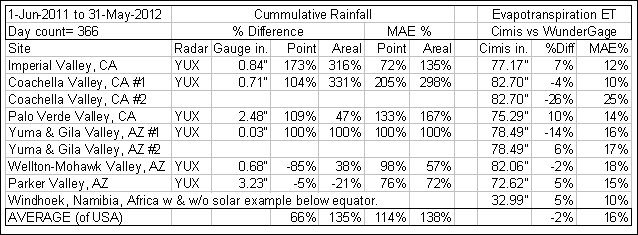
% Difference is the error in total rainfall or toal ET, a
measure of bias.
MAE % is the mean of the individual daily unsigned differences,
a measure of error variablility.
ET:
CIMIS versus Wunderground... Mano y Mano
The California Irrigation Management Information System (CIMIS) is a
program in the California Department of Water Resources that manages a
network of over 130 automated weather stations in the state of California for
the computation of reference Evapotranspiration (ET). ET is the loss of
water to the atmosphere by the combined processes of evaporation (from soil and
plant surfaces) and transpiration (from plant tissues). It is an indicator of
how much water your crops, lawn, garden, and trees need for healthy growth and
productivity.
The standard
ASCE Penman-Monteith reference ET calculation uses the parameters air
temperature, humitity, wind speed, and solar radiation collected at a properly sited automated weather station. The ideal gage siting would be
to centrally locate the station in a large, well-watered turf area that is a
considerable distance from objects that might disrupt wind flow or shade the
station. The terrain surrounding the weather station should be relatively level
if possible.
This comparison is to
evaluate the difference in a properly sited and maintained CIMIS weather gage calculated ET
with solar data to a nearby or not so nearby Wunderground weather gage
which is most likely not
properly sited or maintained and with out solar data. Real-time Wunderground weather gages are located in
thousands of locations around the world that can be used to
calculate ET even without solar radiation info at the Wunder Gage. The
automatic
retrieval, computation, and storage of ET at both sites are made by my program
GetRealtime.exe. Although CIMIS reports their
CIMIS ET it was not used here... err... just because... and ASCE takes a dim
view of these renegades. ;-)

Properly sited and maintained CIMIS weather station above....
versus
Typical Wunderground site and hard to maintain weather station below.

The geographical area selected for comparison are the SUNNY (solar less a
factor in regional regressions used by GetRealtime.exe) irrigated Ag districts along the
Lower Colorado River in Arizona and California. Also, ET tends to be a
concern to those in sunny areas. Although Arizona also maintains
an ET network (AZMET), I have not automated the retrieval of data from their system and so only the CIMIS sites are used here
to see how far is far. Hourly CIMIS data are made
available every 6 hours while AZMET hourlys are only updated daily. If you
would like to automate retrieval and computation of your own weather data go to my
GetRealtime Help page.
A real-time Wunderground weather gage was selected in each of the folowing
agricultural districts for comparison:
1) Imperial Valley, CA (IID)
2) Coachella Valley,CA (CVWD)
3) Palo Verde Valley, CA (PVID)
4) Yuma and Gila Valley, AZ (YCWUA, YID, NGVID)
5) Wellton-Mohawk Valley, AZ (WMID)
6) Parker Valley, AZ (CRIT)
Looking at the above photo of a typical Wunderground gage site, one would expect
higher temperature and lower humidity would increase calculated reference ET.
Windspeed may or may not be higher than the CIMIS 2 meter level. Although
Wunderground participants at the selected sites here do not have photos of their
gages available, zooming in with Google Earth on the Imperial Airport, Yuma Mesa #2,
Wellton-Mohawk, Palo Verde, and Parker Wundergages appear located in open areas
adjacent to irrigated areas and should show better comparisons at first glance
than those located at residences at Coachella #1 and #2, and Yuma Valley #1.
I think we have a better shot at a good outcome than I thought. Let's find out.
(Comparing actual temp, humidity, and wind
speed would be dullsville and would take all the fun out of this first try.
Hmm... I just realized that both CIMIS and Wunderground have historical data to
complete this study in 1 retrieval, but Wunderground stations are here today and
gone tomorrow so let's let this drama play out. And NEXRAD radar rainfall
images are only available for the past 4 hours.)
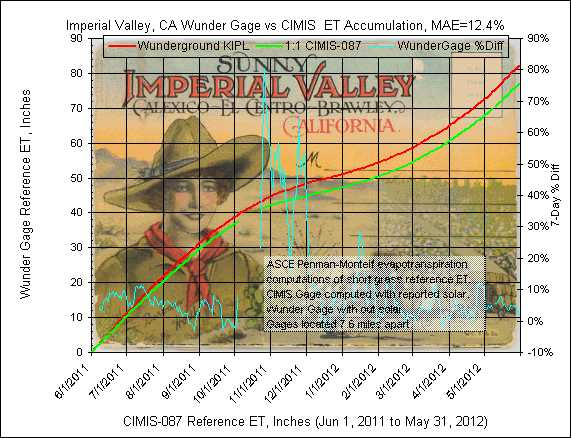
1) Imperial Valley, CA
Wunderground Gage:
KIPL, computation time step=hourly, parameters temp, humidity, wind speed, NO SOLAR.
GetRealtime setup file: KIPL; -27508; ET Grass; Imperial Airport Gage, Ca ET; 0;
32.834,-115.579,-120,-54,0.75; P4 (note the wind speed factor of 0.75 to correct
airport offical 10 m height to 2 m)
CIMIS Gage:
087 Meloland, CA, computation time step=hourly, parameters temp, humidity, wind speed,
solar.
GetRealtime setup file: CIMIS-087; -27538; ET Grass; Meloland, Ca Cimis; 0;
32.81,-115.45,-120,-50,1; P5
The CIMIS gage is located 7.6 miles east of the Wuderground gage.
The
daily graph comparison below includes in the title MAE, mean absolute error, which
is the average of each of the unsigned daily computed ET value difference in
percent..
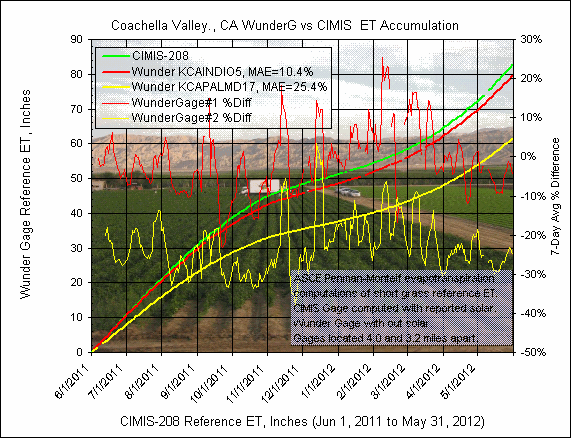
2) Coachella Valley, CA (2 gages)
Wunderground Gage
#1:
KCAINDIO5, computation time step=5 minute, parameters temp, humidity, wind speed, NO
SOLAR.
GetRealtime setup file
#1: KCAINDIO5; -27506; ET Grass; Indio Gage, Ca ET; 0;
33.739,-116.192,-120,1,0.75; P4
CIMIS Gage:
200 Indio II, CA,
computation time step=hourly, parameters temp, humidity, wind
speed, solar.
GetRealtime setup file: CIMIS-200; -27536; ET Grass; Indio Ii, Ca Cimis; 0;
33.75,-116.26,-120,40,1; P5
Wunderground Gage
#2:
KCAPALMD17,
computation time step=15 minute, parameters temp, humidity, wind speed, NO
SOLAR.
GetRealtime setup file #2: KCAPALMD17; -27503; ET Grass; Palm Desert Gage, Ca
ET; 0; 33.739,-116.311,-120,150,1; P4
The CIMIS gage is located 4.0 miles west of Wuderground #1 and 3.2 miles
east of gage #2.
The
daily graph comparison below includes in the title MAE, mean absolute error, which
is the average of each of the unsigned daily computed ET value difference in
percent.
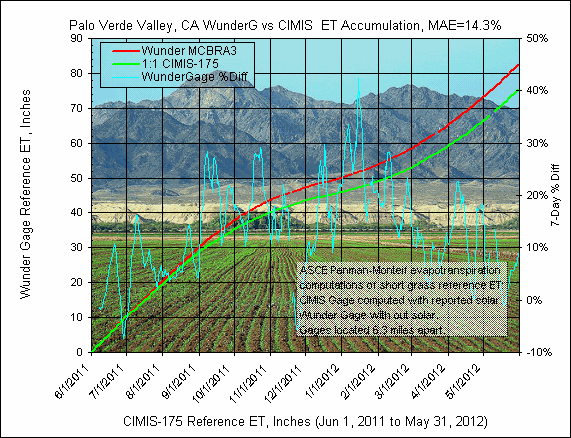
3) Palo Verde Valley, CA
Wunderground Gage:
MCBRA3, computation time step=15 minute, parameters temp, humidity, wind speed, NO
SOLAR.
GetRealtime setup file: MCBRA3; -27509; ET Grass; Cibola Gage, Az ET; 0;
33.304,-114.693,-105,357,0.75; P4
CIMIS Gage:
175 Palo Verde II, CA, computation time step=hourly, parameters temp, humidity, wind
speed, solar.
GetRealtime setup file: CIMIS-175; -27539; ET Grass; Palo Verde Ii, Ca Cimis; 0;
33.39,-114.73,-120,230,1; P5
The CIMIS gage is located 6.3 miles
north of the Wuderground gage.
The
daily graph comparison below includes in the title MAE, mean absolute error, which
is the average of each of the unsigned daily computed ET value difference in
percent.
4) Yuma Valley, AZ (2 gages)
Wunderground Gage:
KAZYUMA11, computation time step=5 minute, parameters temp, humidity, wind speed, NO SOLAR.
KAZYUMA11; -27505; ET Grass; Yuma Valley Gage#1, Az ET; 0;
32.712,-114.666,-105,125,1; P4
CIMIS Gage:
186 San Louis, Mexico, computation time step=hourly, parameters temp, humidity, wind speed,
solar.
GetRealtime setup file: CIMIS-186; -27535; ET Grass; San Louis, Mex Cimis; 0;
32.49,-114.83,-120,48,1; P5
Wunderground Gage:
KAZYUMA16, computation time step=5 minute, parameters temp, humidity, wind speed, NO SOLAR.
KAZYUMA16; -27502; ET Grass; Yuma Valley Gage#2, Az ET; 0;
32.665,-114.633,-105,200,1; P4
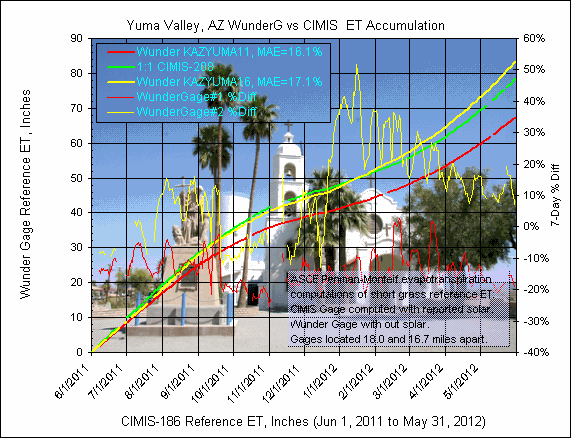
The CIMIS gage is located 18.0 miles south of the Wuderground gage
#1 and 16.7 south of #2.
The
daily graph comparison below includes in the title MAE, mean absolute error, which
is the average of each of the unsigned daily computed ET value difference in
percent..
5) Wellton-Mohawk Valley, AZ
Wunderground Gage:
KAZWELLT4, computation time step=5 minute, parameters temp, humidity, wind speed, NO SOLAR.
GetRealtime setup file: KAZWELLT4; -27504; ET Grass; Wellton Gage, Az ET; 0;
32.691,-114.044,-105,310,1; P4
CIMIS Gage:
201 Andrade, Mexico, computation time step=hourly, parameters temp, humidity, wind speed,
solar.
GetRealtime setup file: CIMIS-201; -27534; ET Grass; San Louis, Mex Cimis; 0;
32.674,-115.044,-120,120,1; P5
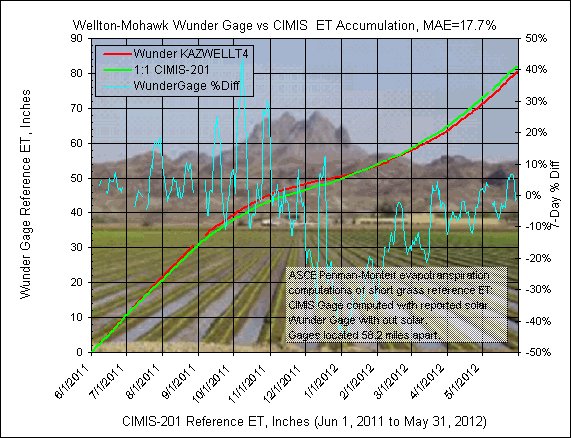
The CIMIS gage is located 58.2 miles west of the Wuderground gage.
The
daily graph comparison below includes in the title MAE, mean absolute error, which
is the average of each of the unsigned daily computed ET value difference in
percent..
5) Parker Valley, AZ
Wunderground Gage:
MTS917, computation time step=5 minute, parameters temp, humidity, wind speed, NO SOLAR.
GetRealtime setup file: MTS917; -27507; ET Grass; Parker Gage, Az ET; 0;
34.131,-114.327,-105,357,1; P4
CIMIS Gage:
135 Blythe NE, CA, computation time step=hourly, parameters temp, humidity, wind speed,
solar.
GetRealtime setup file: CIMIS-135; -27537; ET Grass; Blythe Ne, Ca Cimis; 0;
33.56,-114.67,-120,275,1; P5
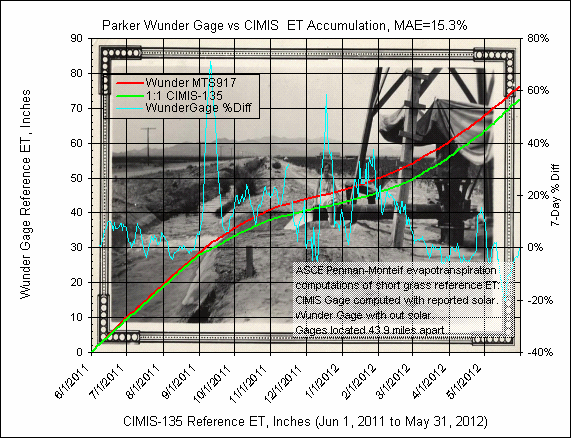
The CIMIS gage is located 43.9 miles south of the Wuderground gage.
The
daily graph comparison below includes in the title MAE, mean absolute error, which
is the average of each of the unsigned daily computed ET value difference in
percent..
ET Example for location below the Equator and ahead in
Time, Windhoek, Namibia, southern Africa:
As an example for setting up GetMyRealtime for another part of the world, a
Wundergage was selected in the southern hemisphere and before Zulu Universal
Time at Greenwich, England.
Wunderground Gage:
INAMIBIA2, computation time step=5 minute, parameters temp, humidity, wind speed,
and with and with out solar for comparison.
GetRealtime setup file w/Solar: INAMIBIA2; 27550; ET Grass; Namibia
Africa w/solar; 0; -22.575, 17.074,15,5488,1; P5
GetRealtime setup file w/o Solar: INAMIBIA2; -27550; ET
Grass; Namibia Africa w/o solar; 0; -22.575, 17.074,15,5488,1; P4
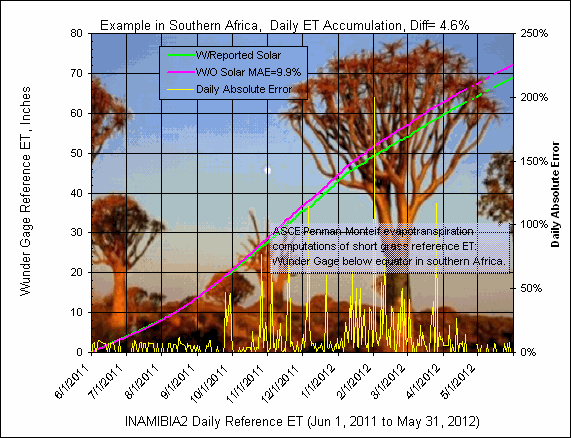
Note that the local standard meridian is +15 and that the latitude is negative
while the longitude is positive, all the reverse of gages in the USA. The
seasons are also reversed so that ET will decrease during the summer... err our
winter... and this station is higher in elevation than Denver, CO but still
pretty arid. Not sure what to make of 42" rainfall for Jan-May, 2011.
This is a WunderGage after all. Looks like the return of the Boojum. And use the
'state' code AZ in the rsite table to turn off northern daylight savings.
(After further review, the 42 inch rainfall was indeed a record and should scare
you Yuman's socks off!)
The comparison for June1 to Nov 1 looks great so far but the rainy season is at
hand with 20 inches of rain typical for the next 5 months and doubt is beginning
to cloud the graph. Geez I hope this works out.
RAINFALL:
Comparison of NEXRAD Radar Point and Areal Rainfall
As long as weather data
is being collected at the above Wunderground gages I
thought I would see how the NEXRAD radar N0R (N0Q after Nov 2011) computed rainfall would compare at
the 6 gages. Also the irrigated area of the 6 ag districts were
palimetered using my
GetMapArea.exee
program and the needed radar boundary files were created for computing district
wide average areal rainfall from the real-time radar images. These
district wide or canal supplying areal radar rainfall data can be used in
real-time by the farmer or district to adjust water orders and save a few bucks.
1) Imperial Valley, CA (IID)
2) Coachella Valley,CA (CVWD)
3) Palo Verde Valley, CA (PVID)
4) Yuma and Gila Valley, AZ (YCWUA, YID, NGVID)
5) Wellton-Mohawk Valley, AZ (WMID)
6) Parker Valley, AZ (CRIT)
The NEXRAD
radar site is YUX south of Yuma, AZ at elevation 250 ft. Rainfall is
computed from the 5-minute N0R images using the standard WRD-88D convective Z-R
relationship using GetRealtime.exe.
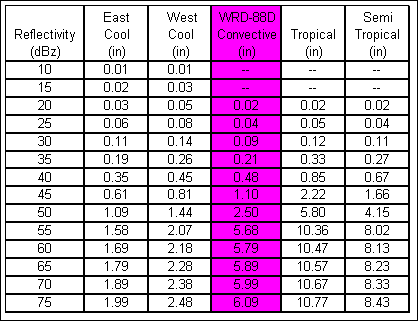
For additional information on NEXRAD radar rainfall using GetRealtime.exe go
here.
1) Imperial Valley, CA
Wunderground Gage:
KIPL, radar distance=58.7 miles, scan elev=4840 ft.
IID repoted irrigated area=1,600 sqmi., rainfall mapped area=3,022
radar pixels or 834
sqmi.
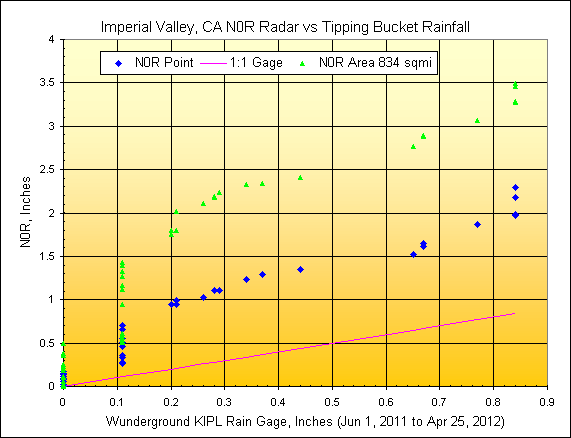
2) Coachella Valley, CA
Wunderground Gage:
KCAINDIO5, radar distance=128.2 miles, scan elev=15,400 ft.
CVWD
reported irrigated area=109 sqmi., rainfall mapped area=694 radar pixels or 182 sqmi.
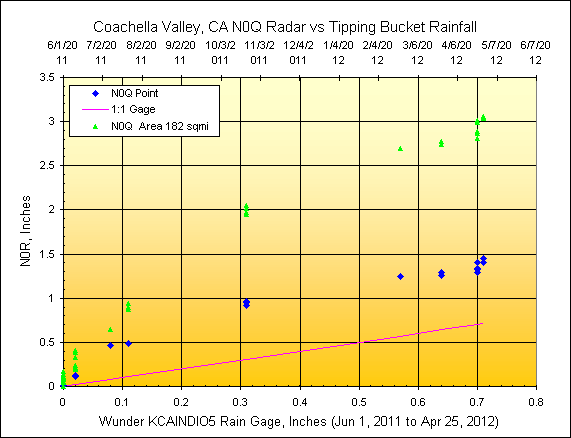
3) Palo Verde Valley, CA
Wunderground Gage:
MCBRA3, radar distance=55.5 miles, scan elev=4,520 ft.
PVID reported irrigated area=163 sqmi., rainfall mapped area=661
radar pixels or 170
sqmi.
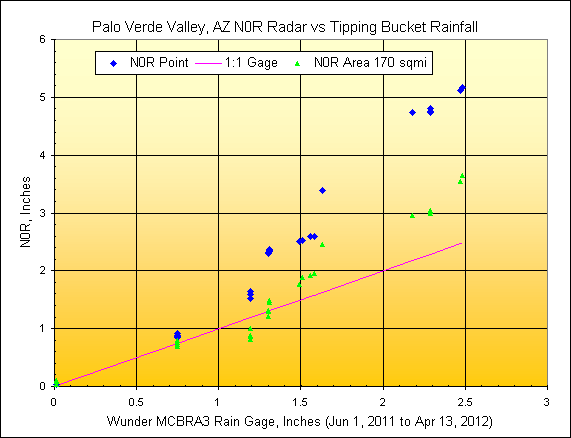
4) Yuma Valley, AZ
Wunderground Gage:
KAZYUMA11, radar distance=14.8 miles, scan elev=1,050 ft.
Yuma Area
reported irrigated area=93 sqmi., rainfall mapped area=523 radar pixels or 125 sqmi.
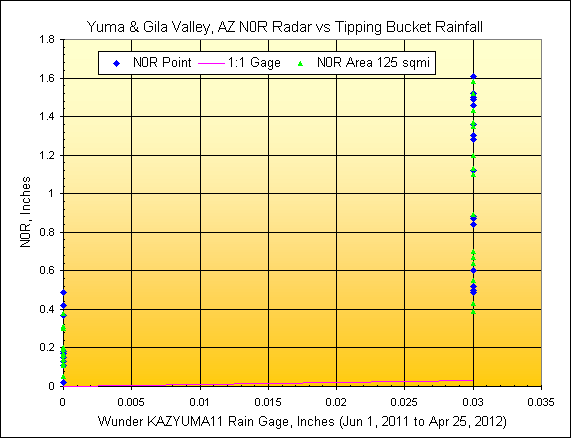
5) Wellton-Mohawk Valley, AZ
Wunderground Gage:
KAZWELLT4, radar distance=37.5 miles, scan elev=2,780 ft.
WMID reported irrigated area=91 sqmi., rainfall mapped area=530
radar pixels or 127
sqmi.
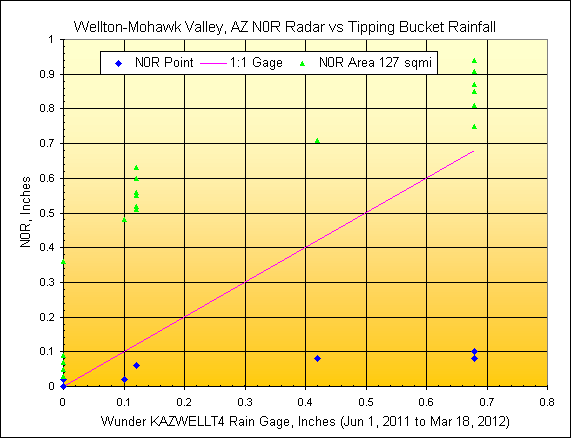
6) Parker Valley, AZ
Wunderground Gage:
MTS917, radar distance=114.1 miles, scan elev=12,730 ft.
CRIT
reported irrigated area=164 sqmi., rainfall mapped area= 569 radar pixels or 150 sqmi.
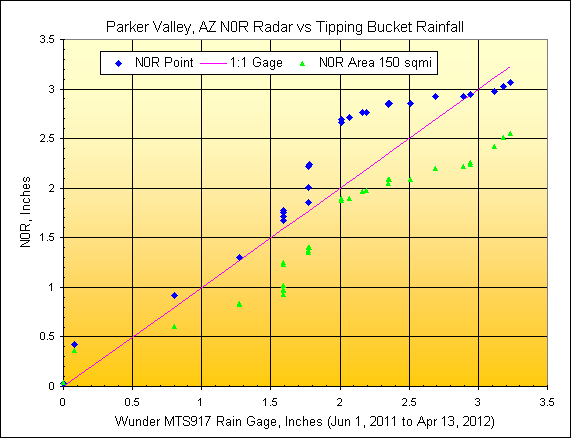
Some additional page links about
ET and Nexrad Radar help and comparisons:
List of How To Videos on Youtube
Help Page for GetNexrad.exe
Nexrad Rainfall to Tipping Bucket Comparison
ET and Radar Rainfall along the Lower Colorado
River, AZ-CA
Nexrad Rainfall-Runoff Comparison Las Vegas
Valley, NV
Nexrad
Rainfall-Runoff Comparison San Jouqin Valley, CA
Nexrad
Rainfall-Runoff Comparisons in northwestern Arizona
Nexrad Snowfall Comparisons in western
central Sierras, CA
Weather Underground is a registered trademark of Weather
Underground, Inc www.wunderground.com

WEBSITE MAP






WU USGS USBR USCS CWRD NWS
More Free Downloads
Comments/Questions
Email: carson@getmyrealtime.com
Label
|